The field of software testing has come a long way. From the early days of manual testing, where human testers verified the software quality, the industry has evolved into a much more dynamic and automated environment. The rise of automated testing allowed teams to test faster and more efficiently, but today’s competitive market demands even more agile, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
This is where Testing as a Service (TaaS) provider comes in—a cloud-based, on-demand testing service that helps organizations simplify their testing processes quickly and easily. TaaS utilizes automation, virtualization, and remote resources to provide flexible testing solutions.
Software firms can contract with the TaaS provider to complete rigorous testing on their projects. In this blog, we’ll explore how testing has evolved, the increasing relevance of TaaS in today’s world, the types of TaaS, and the various advantages of TaaS.
What is Testing as a Service (Taas)?
TaaS stands for Testing as a Service. Testing as a Service (TaaS) is a cloud-based outsourcing solution that allows companies to perform software testing without investing in internal testing infrastructure. Instead of maintaining dedicated in-house teams and tools, organizations can access testing services from a service provider.
With TaaS, businesses can run various tests—such as functional, performance, or security testing—when needed, without worrying about setup or ongoing maintenance. With TaaS testing, you can decide how much work you want to outsource and tackle heavy workloads while optimizing key resources.
Why Do Companies Need TaaS?
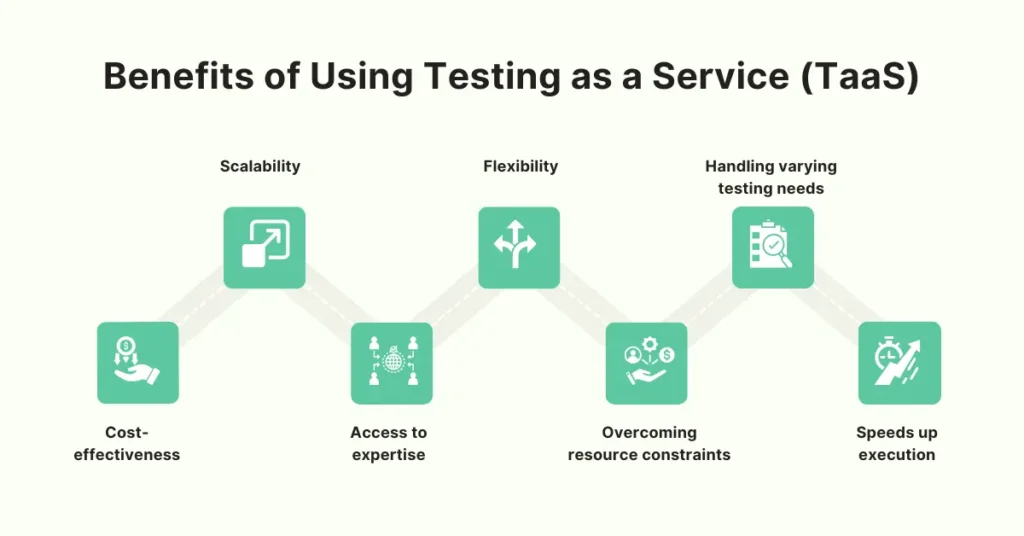 Companies choose TaaS solutions for several key reasons:
Companies choose TaaS solutions for several key reasons:
- Cost-effectiveness: It reduces the need to invest in expensive testing tools and resources, which includes the team.
- Scalability: TaaS can easily scale up or down, depending on the project’s needs.
- Access to expertise: Companies can tap into a global pool of specialized testing skills and technologies they may not have in-house.
- Flexibility: Testing resources can be used on-demand, which helps adjust to changing project requirements quickly.
- Overcoming resource constraints: TaaS helps companies by providing external support when needed and enables them to focus on core business requirements.
- Handling varying testing needs: It allows businesses to handle different testing needs from small updates to major releases, without straining internal resources.
- Speeds up execution: By utilizing cloud-based testing services, companies can accelerate their testing processes, leading to faster delivery of software.
How does Testing as a Service (or TaaS) work?
Testing as a Service (TaaS) operates through various service delivery models that allow businesses to choose the best fit for their needs:
• Managed Testing Services: In this model, a third-party provider handles the entire testing process. They manage everything from planning to execution, providing a comprehensive solution for companies that want to outsource their testing operations.
• On-Demand Testing: This model allows companies to request testing services when needed. It is flexible and ideal for handling projects with last-minute and unexpected changes, helping to find bugs quickly.
• Crowd-Sourced Testing: This model uses a global pool of testers who perform large-scale QA testing in real-life conditions. It is useful for testing across different devices, regions, or user environments, offering a diverse range of testing scenarios.
Integration of TaaS with Agile and DevOps
Testing as a Service enhances Agile and DevOps methodologies, improving the software development lifecycle by ensuring continuous testing and faster feedback loops.
• Agile Methodologies: In Agile environments, TaaS allows for frequent testing as new features are developed. It supports continuous integration and delivery pipelines, ensuring each iteration is tested thoroughly without interrupting the development process.
• DevOps Practices: For DevOps teams, TaaS provides on-demand testing that merges smoothly with automated deployment processes. It ensures high quality through continuous testing and fast feedback during development.
Types of Testing as a Service (TaaS)
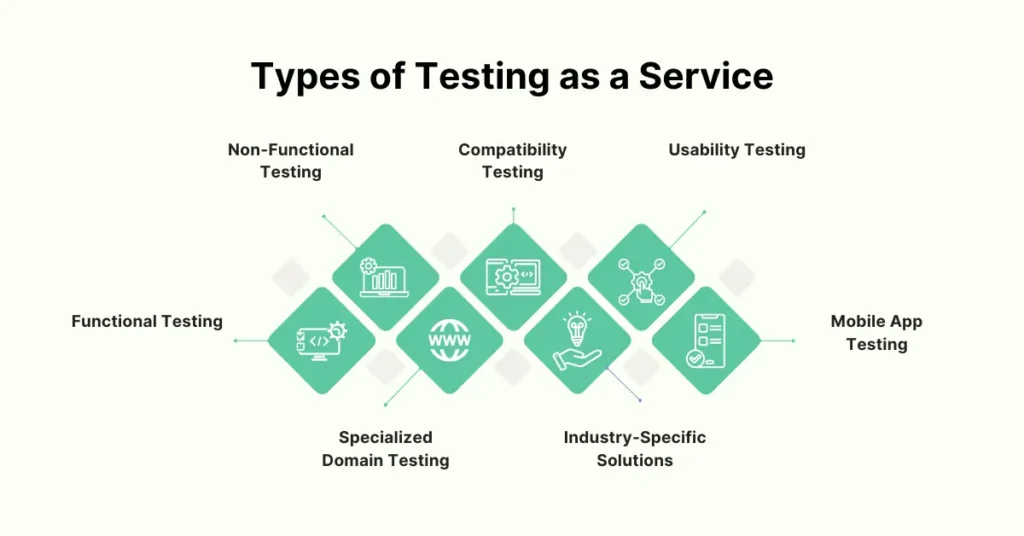 There are different types of TaaS services available in the market:
There are different types of TaaS services available in the market:
• Functional Testing: Checks if each feature of the software functions as expected, ensuring core features work correctly individually and together.
• Non-Functional Testing: Verifies the non-functional requirements of the application. It includes performance testing (how the software performs under load) and security testing (identifying vulnerabilities).
• Specialized Domain Testing: This involves testing an application with a small number of test cases, providing various inputs, and checking if the outputs are correct. It is customized for specific industries, such as healthcare or finance, to meet their unique needs.
• Industry-Specific Solutions: Provides testing services designed for particular industries, addressing their precise needs and standards.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensures that applications run properly across various browsers, devices, platforms, and operating systems.
• Usability Testing: Observes real users as they use a website, app, or digital product to complete tasks, helping to improve the overall user experience.
• Mobile App Testing: Validates the appearance, performance, and functionality of apps across various devices.
Each type of Testing as a Service targets specific testing needs and quality assurance goals, helping ensure that software meets all necessary standards.
Common Use Cases of TaaS
Testing as a Service model is beneficial in various scenarios:
• Startups and SMBs: These organizations need quick and low-cost testing solutions to get testing services on demand, helping them launch their products faster and with less financial risk.
• Enterprises: Large companies face variable testing demands, such as during seasonal peaks. TaaS allows these enterprises to expand or shrink their testing resources as needed, ensuring they can handle peak loads without maintaining a large, permanent testing team.
• Specialized Projects: Some projects, such as those involving mobile apps or IoT devices, need specialized knowledge and skills. TaaS provides access to experts with the skills needed for complex testing, ensuring thorough and accurate results without the need for in-house specialists.
• Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) Pipelines: In current development practices, CI/CD pipelines automate and facilitate the software development and deployment processes. TaaS integrates with these pipelines, providing continuous testing and instant feedback, and maintaining quality while speeding up the development cycle.
Functional Vs Non-functional TaaS
Functional testing ensures that the application’s functions and features work according to business requirements. Non-functional testing examines if the application meets performance and usability expectations from the customer’s viewpoint. Here is a table to explain the differences between functional and non-functional TaaS:
| Aspect | Functional TaaS | Non-Functional TaaS |
| Purpose | Validates if the software functions as expected. | Tests attributes such as performance, security, and usability. |
| Focus | Core features and functionality of the application. | How the application performs under certain conditions or constraints. |
| Examples | Checking if a login system works correctly. | Evaluating the application’s response time under load. |
| Testing Types | Unit testing, integration testing, system testing. | Performance testing, security testing, usability testing. |
| Goals | Ensure that all functionalities work as intended. | Ensure the software meets performance, security, and user experience standards. |
| Timing | Typically done early in the development process. | Often done towards the end or in parallel with functional testing. |
Benefits of TaaS
Testing as a Service offers several key advantages. It speeds up software releases, provides better testing across different platforms, and scales to fit your needs. TaaS also gives you access to advanced tools and expertise, all the while being cost-effective.
- Reduced Time-to-Market: Speeds up the software release process by providing efficient and flexible testing services.
- Improved Testing Coverage: Ensures extensive testing across various platforms and environments, catching more issues.
- Enhanced Scalability: Easily scales to handle large-scale testing needs, accommodating growth and peak loads.
- Access to Advanced Tools: Provides access to the latest testing tools and technologies without internal investment.
- Cost Savings: Maximizes resource use by reducing costs related to maintaining in-house testing infrastructure and teams.
- Faster Deployment: Enables quicker testing cycles, allowing for faster software deployment and updates.
Disadvantages of Testing as a Service (Taas)
Adopting TaaS also comes with a lot of challenges, such as data security concerns, dependency on external providers, and the need for seamless integration with development processes
Here are some common challenges of Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS):
- Data Security and Privacy: Sharing sensitive data with third-party providers can raise concerns about security and compliance.
- Customization Limitations: Pre-defined testing environments may not fully meet specific business requirements.
- Integration Issues: Integrating TaaS with existing tools and workflows (e.g., CI/CD pipelines) can be complex.
- Communication Gaps: Working with external teams can sometimes lead to miscommunication or delays in feedback.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Cloud-based TaaS solutions rely heavily on stable internet connections for smooth operations.
- Vendor Lock-in: Relying too much on one TaaS provider can limit flexibility and make switching providers difficult.
Best Practices of Testing as a Service
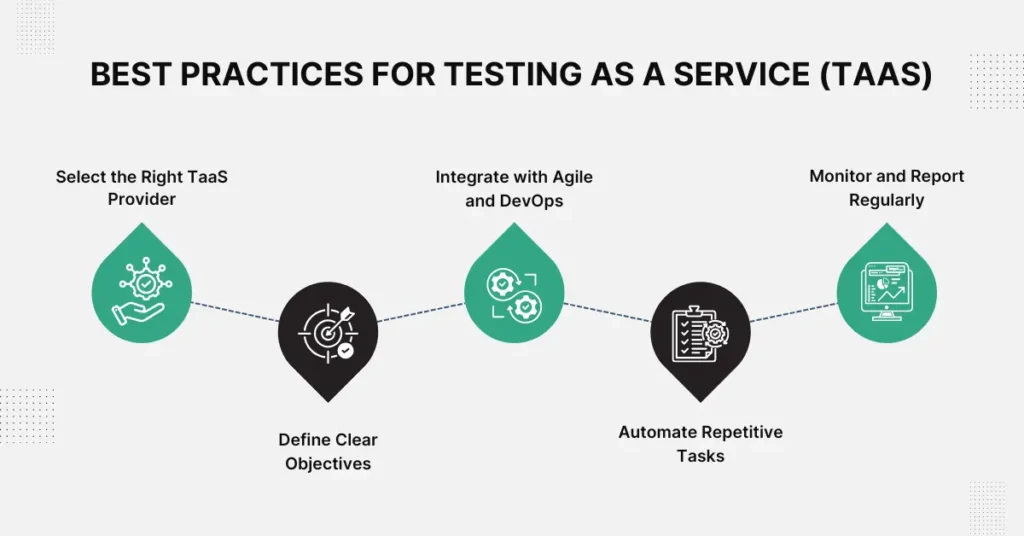
• Select the Right TaaS Provider: Choose a TaaS provider that matches your project’s specific needs, including expertise, technology, and scalability. Evaluate their track record, service offerings, and pricing, and ensure they can meet your testing requirements effectively.
• Define Clear Objectives: Clearly outline what you want to achieve with testing, including specific goals, success criteria, and performance benchmarks. This sets a road map to align with your project objectives and ensures that all key aspects are covered for the desired results.
• Integrate with Agile and DevOps: Incorporate TaaS into your Agile and DevOps workflows. This allows for continuous testing and integration, enabling teams to build, test, and release software faster and more accurately.
• Automate Repetitive Tasks: Implement automation for tasks that are repetitive or time-consuming. This improves reliability, reduces human error, and speeds up workflow, saving time and money.
• Monitor and Report Regularly: Regular monitoring of progress and detailed reporting help to identify issues early. It helps in evaluating testing strategies and making informed decisions based on the testing results.
Conclusion
In summary, Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS) offers a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for modern software testing needs. Whether yours is a startup needing rapid deployment, an enterprise facing changing demands, or a project needing specialized skills, TaaS provides valuable benefits such as faster time-to-market, better testing coverage, and access to advanced tools.
QA Touch can further simplify your testing processes by offering a broad platform that integrates seamlessly with your testing solutions. It helps in managing test cases, tracking defects, and improving collaboration across your team, making it an ideal complement to your testing strategy.
We’d love to hear how QA Touch can support your testing needs. Feel free to start your 14-day free trial or discuss your specific requirements!










