https://register.qatouch.com/?ref=blog_how_to_write_qa_test_summary_report_b1The whole QA testing is attaining great prominence like never before – A reliable, quality-guaranteed tech procedure. Have you ever thought about how to write a QA test summary report sample?
Meanwhile, how you report your insights is also paramount. Recording details from the fundamentals to the results you think are overwhelming. That’s untrue. It can be accessible, competent, and understandable at the same time.
If you are wondering how to write a comprehensive final test summary report, you are googling it at the right place.
What Is A QA Test Summary Report Sample?
Alright, it does something beneficial. But, wondering what?
A test summary report is a detailed overview containing every important detail identified and discovered from different testing stages. The undeniable reason is to deliver the high/low performance of the software test to the respective stakeholders. So, the basic idea is to add value to their decision-making on whether to go live or not.
And it indeed enables the project manager to assess the effective test plan execution, ensuring transparency and accountability.
The report would include the product quality of the software in different environments, the quality of testing efforts, and statistics obtained from incident reports.
What Makes A Good QA Test Summary Report Sample?
The following are the bases of a solid test summary report:
- Specification: You don’t have to produce a lengthy test report summary. It should include all of the efficient test result parameters concisely and clearly.
- Standard: The test summary report should stick to a consistent template since it is simple for stakeholders to study and understand.
- Clarity: The test report should provide correct information. The report should be brief and understandable.
- Detail: Wherever possible, the final report should provide detailed information regarding the testing efforts. Even though it is brief, the information doesn’t have to be abstract because that won’t allow the stakeholders to understand it clearly.
What Should A Test Summary Report Include?
A test report summary that is instructive should be concise and relevant. There are numerous examples of test summary report templates online, but not all of them may be suitable for your case. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the report after doing a thorough study following the features of our test project.
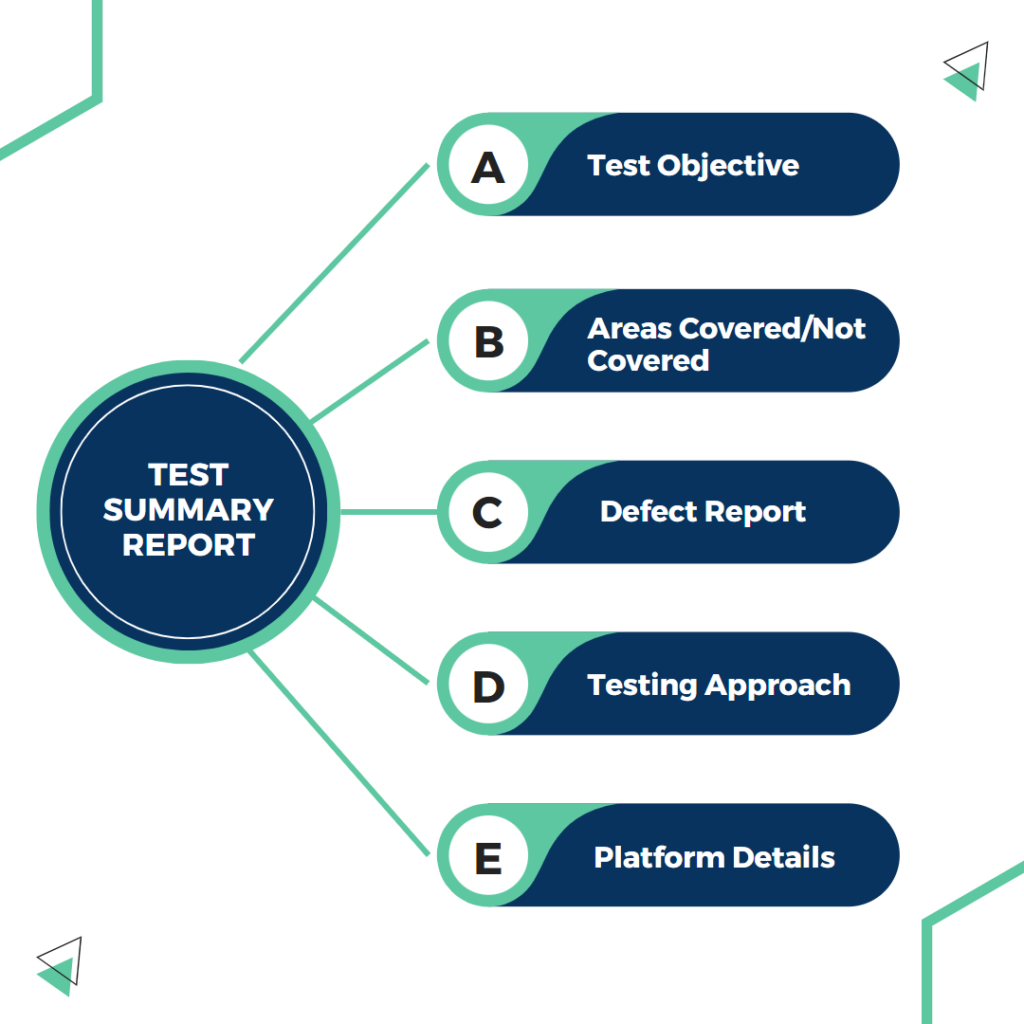
Here is a list of what should be included:
- Test Objective: Specify the testing objectives; doing just that shows the team members understood the test objective and the requirement.
- Areas Covered: Include the tested product areas and features. Although it doesn’t have to cover every test scenario in great detail, it should at least cover all the major ones.
- Areas Not Covered: It is crucial to document the product features that were not tested. Any areas not tested can cause concern on the client’s end. So, you need to ensure that anything untested is highlighted and that expectations are set appropriately. Be careful to provide a reason for your main points, such as a limitation on access or a shortage of devices.
- Testing Approach: This is crucial to discuss because it explains what was tested and how it was done. Make sure to describe in detail the corrective action taken and the different testing strategies used to complete the task.
- Defect Report: Although a defect report is typically included in a bug report, having one in the test summary report can offer your test report an edge.
- Platform Details: Products are currently tested on a variety of platforms. Due to the increased demand, not only a testing process now includes various device setups and browsers but also various software releases. Let’s be sure to provide information about each platform and environment in which the product was tested in.
- Overall Summary: The purpose is to offer feedback on the overall state of the application under test. For the customer to determine how near they are to ship the product to them, it should notify them of any critical issues that were found and how many are still outstanding.
How To Create An Outline Of The Test Report?
Generally, this may differ from company to company based on your testing exercises. However, below are the few traditional essentials of a test summary report.
- A short evaluation of how well the testing is performed.
- Quality of testing effort.
- Quality assessment of the software.
- The recordings should also include the factors like time taken, and different environments tested.
- The incident reports included statistics.
- A brief on the final test results.
1. Project And Product Info
Mention the chunks of information about the project and product. For instance, the project name, official/preferred product name, and version of the particular product.
2. Purpose
Mention a short explanation of the objective behind making the report. Example: The following report is a brief of all the insights uncovered during the different testing phases of the ABC project.
3. Software/Product Overview
Consider it as a short intro to the product. You can follow the below example as a reference.
Productimize is a web-based product customization platform catering to e-commerce businesses worldwide. It helps the clients to design their products increasing business sales by 40%. Bountiful features like 3D visualization, text input, image rendering, social sharing, and product personalization are revolutionary. Industries like furniture, Jewellery, Home goods, print and promotions, and sporting goods are benefited from this product.
4. Objective And Testing Scope
This segment allows the stakeholders to understand the functions in and out of scope for testing—information on items not tested and also why aren’t they tested. Restrictions, hurdles, and learnings in each stage are also mentioned.
Example: A verification that compels third-party connectivity wasn’t possible. It happened due to some technical problem and should be resolved soon.
Pay attention to this section, and it shouldn’t be left incomplete. If left unwritten, the stakeholders will provide complete misinformation. They would acknowledge that all the different tests are completely zero issues. And finally, the decision-making will end at stake.
5. Magical Metrics
So far, the most interesting and important one. The critical metrics in visual representation allow a requisite understanding of some complex data. The graphics, in general, are the best for a better understanding of anything.
Metrics like:
- A number of test cases passed vs. failed.
- Cases planned vs. executed.
- Total defects found, their severity, and their status.
- Module-wise defects distribution.
6. Types Of Testing
The information on prolific testing was performed for a specific project. It is to make sure that all the testing is conducted as agreed earlier in the strategy. Prime examples are as follows.
- Smoke Testing
- Regression Testing
- System Integration Testing
a) Smoke Testing: This testing is done if a build is received to ensure the crucial functionalities are working fine. First, accept the build and further can start the testing.
b) Regression Testing: This testing is carried out every time the build is established for testing. It contains defect fixes and new improvements if available. It is performed on the complete software, not just on a specific functionality or defect fixes.
It works amazingly to ensure rich functionality after the new defect fix, and further improvements are attached to the existing software. New test cases of the new feature can be added and executed.
c) System Integration Testing: This testing is done to rectify if the whole software performs well, basing the requirements without any errors. When the business scenarios are tested, it ensures that the essential functions are performing as planned.
7. Testing Environments
The various details of the testing environments should be recorded here, with accurate data. Follow the below format:
- Application URL
- Server
- Database
- Tools used example: Quality Centre ( HP ALM )
8. Lessons Learned
This is a non-fancy section for lessons learned, not for the stakeholders. Post the problem faced and solutions found, and crucial decisions made throughout. These recorded mistakes can be avoided in the next testing encounter. Examples: The issue faced – Manual testing is a problem in the smoke test cases. Solution – The number of test cases was automated, and the scripts executed saved time.
9. Recommendations And Improvements
Any recommendations you feel can add strength to the testing of the software can be made here. Example: Better test management tools with valuable integrations can be used for quick and swift testing.
10. Test Results
A detailed inventory of all functionalities checked and the defects found.
- Details about test case results also should include links to issues of only failed and blocked test cases.
- No. of bugs found.
- Status of bugs. (opened, resolved, and depending)
- List it by severity and priority.

11. Exit Criteria
It’s more of a yes or no section with the most predominant details. It is defined as completing testing by meeting all the planned requirements. Examples are as follows:
- Plan the number of test cases executed – Yes
- The defects and all kinds of severity are entirely verified and closed – Yes
Again this may differ from project to project and company to company.
12. Conclusions
This segment mentions whether the team members stand to go live. If the software testing didn’t meet the exit criteria, say it as follows.
The application/software is not suggested to go live.
If the software meets the exit criteria by fulfilling all the requirements, then suggest it as follows.
The application/software met the exit criteria satisfying the requirements mentioned in section 9, so we suggest the software/application go live.
13. Definition, Abbreviation, And Acronyms
A QA test summary report is to communicate the complex test process and its outcome to the stakeholders.
Sometimes the stakeholders may not be familiar with all the terms used in the report. It is better to give them that knowledge in the report itself. Making communication easy is as important as the testing process itself. Also, please don’t make a report full of engineering terms; not every stakeholder is an engineer to understand them.
Stakeholders, upper management staff, and concerned clients will view this artifact document. It is crucial to provide the facts and information about the software testing done, its performance, and its conclusions.










