Prompt Engineering for Testers: A New Skillset for the AI Era
AI-powered tools are transforming the way testers work. From generating test cases to creating test data and summarizing defects, AI can automate many time-consuming tasks. But there’s a catch- the quality of AI’s output depends heavily on the input it receives. This is where prompt engineering comes in, a skill that every modern QA tester should develop to get the most out of AI tools. In this blog, let us understand what prompt engineering is, why it’s becoming essential for testers, and how you can craft better prompts to improve your testing workflow.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the art and science of designing and refining the instructions, or prompts, you give to an AI model. The goal is to craft these prompts in a way that guides the AI to produce the most accurate, relevant, and useful responses possible. Simply put, it’s about knowing how to ask the AI to get the best answers for your specific needs.
How Prompt Engineering Works
Large language models (LLMs), such as those powering many AI tools today, don’t understand language the way humans do. Instead, they analyze the words and structure of your prompt to predict and generate the most probable next words or sentences. This means the way you phrase your prompt- your choice of words, the context you provide, and the level of detail- directly impacts the quality of the AI’s response.
For example, a vague prompt like “Write test cases” may produce a very generic list. But a prompt that clearly states, “Write detailed functional test cases for the login feature of a mobile banking app, including edge cases for password input,” will result in a far more targeted and valuable output. Context and specificity help the AI understand exactly what you’re looking for.
Why It’s Relevant in Software Testing
Testers are increasingly relying on AI-powered tools to generate test artefacts such as test cases, test data, and defect summaries. However, these AI outputs are only as good as the prompts they receive. Without effective prompt engineering, testers risk receiving incomplete, irrelevant, or low-quality results that require significant manual correction.
Learning prompt engineering empowers testers to communicate precisely with AI tools, enabling them to produce high-quality test artefacts efficiently. This skill enables QA professionals to fully understand the potential of AI, reduce manual effort, and enhance overall testing accuracy and effectiveness.
Why Prompt Engineering is a Critical Skill for Testers
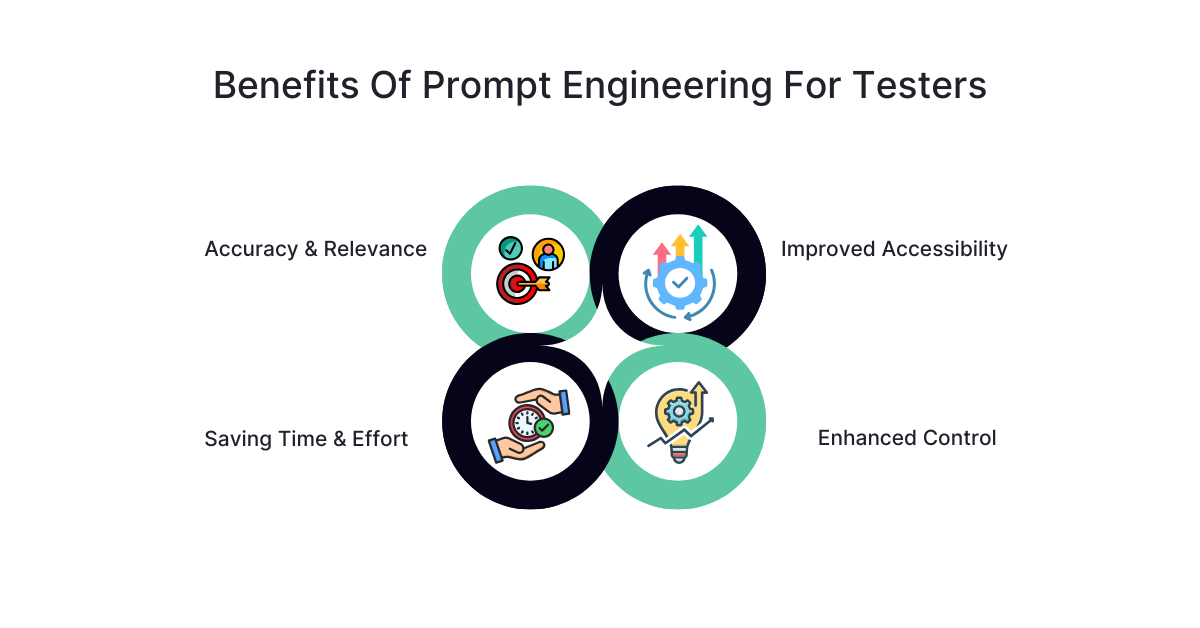
As AI-powered tools become more common in software testing, mastering prompt engineering is no longer optional; it’s essential. Here’s why testers should prioritize developing this skill:
The Rise of AI-Augmented Testing
Testing workflows are evolving to incorporate AI technologies that automate routine but important tasks such as generating test cases, creating test data, and analyzing defects. These AI tools help testers save time and increase coverage, but their effectiveness depends heavily on the quality of the prompts they receive.
Well-crafted prompts directly translate into more accurate, relevant, and comprehensive AI-generated outputs, improving overall productivity and reducing manual rework.
Ensuring Quality of AI Outputs
Vague or poorly structured prompts often lead to AI outputs that are incomplete, irrelevant, or overly generic. This can result in test artifacts that require significant manual revision, negating the efficiency benefits of AI.
Prompt engineering helps maintain the quality of AI-generated work by ensuring that the instructions given are clear, detailed, and context-aware- producing results that are ready for immediate use or require minimal editing.
Empowering Testers to Collaborate with AI
Prompt engineering turns AI from a passive tool into an active collaborator. By learning how to communicate their requirements precisely, testers can guide AI models to generate outputs that align with business priorities, domain specifics, and testing strategies.
This collaborative approach allows testers to utilize AI’s strengths while maintaining control over quality and relevance, making AI a powerful partner in the testing process.
Applications of Prompt Engineering in Testing
Prompt engineering can significantly enhance various QA tasks by helping AI deliver precise, actionable outputs. Here are some key areas where mastering prompt crafting makes a real difference:
Crafting Prompts to Generate Test Cases
When you ask AI to generate test cases, the clarity and detail in your prompt make all the difference. Instead of giving a vague instruction like, “Generate test cases for login,” try to be specific about the features and scenarios you want covered. For example:
“Generate detailed functional and negative test cases for a web application login page that includes username, password, CAPTCHA, and ‘Forgot Password’ functionality. Cover valid and invalid inputs, error messages, and edge cases.”
This kind of prompt helps AI produce comprehensive and relevant test cases that save you time and reduce manual corrections.
Crafting Prompts to Create Test Data
Generating realistic and varied test data can be a challenging and time-consuming process. With AI, you can guide it to create exactly the kind of data you need by specifying formats, constraints, and special conditions. For example, you might ask:
“Create 15 user profiles with valid and invalid email addresses, phone numbers, and postal codes for testing a global e-commerce platform. Include edge cases like missing fields and special characters.”
By providing this level of detail, you’ll get diverse and useful test data that helps uncover hidden defects.
Crafting Prompts to Summarize Defects
Sorting through numerous defect reports can be overwhelming. By prompting AI effectively, you can get concise summaries and organized categories that help prioritize work. For instance:
“Analyze these defect reports and provide a summary highlighting the main issues, severity levels, and categorize defects into UI, functionality, and performance-related bugs.”
This empowers you to quickly understand defect trends and communicate clearly with your team and stakeholders.
Examples of Effective Prompts for Testers
To help you put prompt engineering into practice, here are some real-world examples of well-crafted prompts you can use in your QA tasks. Notice how these prompts are clear, specific, and provide enough context to guide the AI toward useful outputs.
Example Prompts for Test Case Generation
When generating test cases, be as specific and detailed as possible to guide the AI effectively. Tell the AI exactly what functionality you’re testing, what kind of test cases you want, and any constraints.
Good examples:
- “Generate a list of functional and negative test cases for the checkout process of an e-commerce website, covering guest checkout, logged-in users, invalid payment methods, and edge cases.”
- “Write end-to-end test scenarios for a mobile banking app’s ‘Funds Transfer’ feature, including scenarios for insufficient balance, invalid account number, and transaction confirmation.”
Poor example:
- “Write test cases for funds transfer.”
This is too general and will likely return incomplete or irrelevant results.
Example Prompts for Test Data Creation
Creating diverse, realistic test data is crucial for uncovering bugs. Here’s how you can instruct AI clearly:
Good examples:
- “Generate 20 customer profiles with a mix of valid and invalid email addresses, phone numbers, and postal codes for testing an online retail application. Include edge cases like missing fields, very long names, and special characters.”
- “Provide sample input data for testing a date of birth field, including valid dates, leap year dates, dates in the future, and invalid formats.”
Poor example:
- “Generate some test data.”
This leaves too much to interpretation and won’t produce targeted results.
Example Prompts for Defect Summarization
You can also use AI to help you summarize and categorize defects efficiently. These examples show you how:
Good examples:
- “Analyze the following bug reports and summarize the top three recurring issues, noting their severity and affected modules.”
- “Categorize these defects into UI, functionality, performance, and security issues, and provide a one-line summary for each.”
- “Review the defect logs below and suggest potential root causes and recommended next steps.”
Poor example:
- “Summarize these defects.”
Again, too vague to guide the AI effectively.
Common Mistakes in Prompting AI (and How to Avoid Them)
Even experienced testers can fall into some common traps when crafting prompts for AI tools. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can avoid frustration and get more accurate, useful outputs.
Being Too Vague
One of the most frequent mistakes is writing overly general prompts, such as “Write test cases” or “Summarize defects.” The problem with vague prompts is that AI will give you equally vague, generic, or incomplete responses because it doesn’t know exactly what you’re asking for.
That is why you should always specify the feature, the type of output you want, and any relevant details.
Overloading the Prompt
On the other extreme, some testers try to include everything in a single, very long prompt- listing dozens of requirements or mixing unrelated tasks. This can overwhelm or confuse the AI, leading to disorganized or incomplete results.
You must break down complex tasks into smaller, focused prompts. If you have multiple objectives, handle them one at a time. For example, generate test cases first, then create test data, then summarize defects- each with its own clear prompt.
Ignoring Context
Another common mistake is assuming the AI already understands the system under test, the domain, or the expected level of detail. Without proper context, the AI may make incorrect assumptions or deliver irrelevant results.
Always ensure that you provide domain information, the scope of the feature, and any relevant constraints.
Best Practices for Prompt Engineering in Testing
To help you get the most out of AI tools, here are some proven best practices you can follow when crafting prompts. These tips will help you generate more accurate, useful, and relevant outputs for your testing tasks.
Be Clear and Specific
The clearer and more specific your prompt is, the better the AI can understand what you need. Avoid vague or generic language that leaves room for interpretation.
Spell out exactly what functionality, scenarios, and edge cases you want the AI to cover. For example:
“Generate 10 negative test cases for the login feature, focusing on invalid usernames, invalid passwords, empty fields, and SQL injection attempts.”
Provide Context and Constraints
AI doesn’t inherently know your domain, the system under test, or the business rules- unless you tell it. Supplying context and setting boundaries helps the AI tailor its output to your needs.
Include information such as the type of application (web, mobile, API), the domain (banking, healthcare, retail), and any constraints (e.g., formats, standards, localization requirements).
Iterate and Refine
Prompting is not a one-and-done process. Sometimes your first prompt won’t produce perfect results- and that’s okay. Treat it as an iterative process.
Start with a draft prompt, review the output, identify gaps, and adjust the prompt accordingly. Over time, you’ll learn what phrasing works best for your specific use cases.
Use Examples in Your Prompts
Including examples of the output you’re looking for can help the AI understand the structure and level of detail you expect.
If you want test cases in a specific format, add a short example to the prompt. For example:
“Generate test cases for the checkout process. Format each test case as: [Test Case ID], [Description], [Expected Result]. Example: TC_01: Verify successful purchase with valid credit card. Expected Result: Order confirmation is displayed.”
Courses To Learn Prompt Engineering
If you’re ready to build your prompt engineering skills and apply them effectively in QA, there are several resources, both paid and free, that can help. Here, have a look:
Free Courses
- Google’s 9 Hour AI Prompt Engineering Course
- DeepLearning.AI- “ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers”
- Prompt Engineering for ChatGPT
Paid Courses
- Prompt Engineering Courses On Coursera
- Prompt Engineering Courses on Udemy
- Introduction to Prompt Engineering
The Future of Prompt Engineering in QA
As AI technology continues to advance, the way testers interact with AI will also evolve. Prompt engineering is not just a passing trend- it’s becoming a foundational skill for QA professionals. Here’s what the future might look like:
Moving Toward More Conversational Testing
In the future, you may no longer need to craft a perfect, detailed prompt all at once. Instead, testers are likely to engage in conversational, iterative interactions with AI, similar to having a dialogue with a colleague.
- You could start with a general request, review the AI’s response, and then refine or redirect it based on what you see.
- This back-and-forth style of testing will make AI tools even more user-friendly and powerful for creating test cases, generating data, and analyzing defects
Prompt Libraries and Templates
As more organizations embrace AI in testing, we can expect to see shared prompt libraries and templates become common practice.
- Teams will likely develop collections of proven, domain-specific prompts for recurring QA tasks, which testers can reuse and adapt instead of starting from scratch.
- These libraries will save time, ensure consistency, and help new team members get up to speed faster.
Combining Prompt Engineering with Domain Expertise
No matter how sophisticated AI becomes, your domain knowledge and testing expertise will remain critical. AI can assist you, but it relies on you to guide it effectively.
- Understanding the business context, edge cases, and quality goals of your application, and then translating that knowledge into clear prompts- is what will set great testers apart.
- The best results will come from testers who combine strong prompt engineering skills with a deep understanding of the systems and users they serve.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering is becoming a valuable skill for QA testers in the era of AI. Using AI tools to craft clear, context-rich prompts, you can automate and enhance tasks such as test case generation, test data creation, and defect analysis. This not only boosts productivity but also ensures higher quality outcomes.
QA Touch is an efficient test management platform that supports these evolving workflows by seamlessly integrating AI capabilities, empowering testers to adopt this new skill set confidently.
Ready to get started? Sign up on QA Touch to help your team master prompt engineering and elevate your testing processes.